Matching (Value 10)
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below.
a. | anode | d. | half-cell | b. | battery | e. | cathode | c. | fuel
cell |
|
|
|
1.
|
the electrode at which oxidation occurs
|
|
|
2.
|
one part of a voltaic cell in which either oxidation or reduction
occurs
|
|
|
3.
|
the electrode at which reduction occurs
|
|
|
4.
|
a group of cells that are connected together
|
|
|
5.
|
a voltaic cell in which a fuel substance undergoes oxidation and from which
electrical energy is obtained continuously
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | electrode | d. | voltaic cell | b. | electrolysis | e. | dry cell | c. | salt
bridge |
|
|
|
6.
|
a tube containing a conducting solution
|
|
|
7.
|
a conductor in a circuit that carries electrons to or from a substance other
than a metal
|
|
|
8.
|
an electrochemical cell that is used to convert chemical energy to electrical
energy
|
|
|
9.
|
a voltaic cell in which the electrolyte is a paste
|
|
|
10.
|
a process in which electrical energy is used to bring about a chemical
change
|
Multiple Choice (Value 30) including two bonus questions.
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers
the question.
|
|
|
11.
|
Which metal is the most easily oxidized?
a. | highly active metal | c. | slightly active metal | b. | moderately active
metal | d. | an inactive
metal |
|
|
|
12.
|
Of the following metals, which ions are most easily reduced?
a. | iron | c. | aluminum | b. | mercury | d. | potassium |
|
|
|
13.
|
Which of the following metals is oxidized by calcium ions?
a. | potassium | c. | iron | b. | zinc | d. | lead |
|
|
|
14.
|
Which metal ion is reduced by lead?
a. | potassium | c. | mercury | b. | calcium | d. | cadmium |
|
|
|
15.
|
Which ion can be most easily reduced?
|
|
|
16.
|
Identify the pair of metals that lists the more easily oxidized metal on the
left.
a. | Ag, Na | c. | Ca, Al | b. | Fe, K | d. | K, Li |
|
|
|
17.
|
The first electrochemical cell was invented by ____.
a. | Michael Faraday | c. | James Maxwell | b. | Alessandro Volta | d. | Benjamin
Franklin |
|
|
|
18.
|
What happens in a voltaic cell?
a. | Chemical energy is changed to electrical energy. | b. | Electrical energy is
changed to chemical energy. | c. | Electrical energy is changed to magnetic
energy. | d. | Magnetic energy is changed to electrical energy. |
|
|
|
19.
|
At which electrode does oxidation occur in a voltaic cell?
a. | anode only | b. | cathode only | c. | both anode and
cathode | d. | either anode or cathode, depending on the metal |
|
|
|
20.
|
Which electrode is labeled as positive in a voltaic cell?
a. | anode only | c. | both anode and cathode | b. | cathode
only | d. | neither anode nor
cathode |
|
|
|
21.
|
A zinc-copper cell is constructed: Zn | Zn 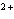 (1 M) || Cu 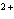 (1 M) | Cu. What occurs to the mass of the copper electrode as the reaction
proceeds? (Zinc is above copper in the activity series of metals.) a. | It decreases. | c. | It remains the same. | b. | It increases. | d. | cannot be
determined |
|
|
|
22.
|
What balances charges that may build up as reduction and oxidation occur in a
voltaic cell?
a. | the salt bridge | c. | the electrolyte solutions | b. | one of the
half-cells | d. | the moving
electrons |
|
|
|
23.
|
In a dry cell, the electrolyte is a ____.
a. | solid | c. | liquid | b. | paste | d. | gas |
|
|
|
24.
|
What metal is oxidized in the most common dry cell?
a. | copper | c. | iron | b. | zinc | d. | carbon |
|
|
|
25.
|
What is reduced in the most common dry cell?
a. | copper | c. | manganese dioxide | b. | zinc | d. | carbon |
|
|
|
26.
|
What electrolyte is used in a lead storage battery?
a. | hydrochloric acid | c. | lead acetate | b. | sulfuric acid | d. | lead nitrate |
|
|
|
27.
|
Why can’t a lead storage battery be recharged indefinitely?
a. | A direct current must pass through the cells. | b. | The electrodes lose
lead sulfate. | c. | It is difficult to reverse the direction of current flow. | d. | The electrolyte is
too expensive. |
|
|
|
28.
|
How is a lead storage battery recharged?
a. | A direct current is applied to it. | b. | A magnet is held close to
it. | c. | Alternating current is forced through it. | d. | The pressure on it
is increased. |
|
|
|
29.
|
What happens in a hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell?
a. | Oxygen diffuses through the cathode. | b. | Oxygen diffuses through the
anode. | c. | Hydrogen diffuses through the cathode. | d. | Hydrogen and oxygen are mixed before entering
the anode. |
|
|
|
30.
|
Which of the following is true about fuel cells?
a. | They only produce energy in short bursts. | b. | They are
inexpensive. | c. | They have never been built or used. | d. | They can be designed so that they emit no
pollutants. |
|
|
|
31.
|
What is the cell potential?
a. | the difference in reduction potentials of the half-cells | b. | the difference in
oxidation potentials of the half-cells | c. | the sum of reduction potentials of the
half-cells | d. | the sum of oxidation potentials of the half-cells |
|
|
|
32.
|
What standard reduction electrode has a half-cell potential of 0.00 V?
a. | oxygen | c. | lithium | b. | hydrogen | d. | fluorine |
|
|
|
33.
|
If the standard reduction potential of a half-cell is positive, which redox
reaction is spontaneous when paired with a hydrogen electrode?
a. | oxidation | c. | both a and b | b. | reduction | d. | neither a nor b |
|
|
|
34.
|
What is the relative standard reduction potential of the half-cell in which
reduction occurs?
a. | positive | b. | negative | c. | more negative than
the other half-cell | d. | more positive than the other
half-cell |
|
|
|
35.
|
Which metal will react spontaneously with Cu 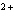 ( aq) at 25 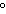 C?
|
|
|
36.
|
Which electrode (anode or cathode) is designated as positive in an electrolytic
cell?
a. | anode | c. | both | b. | cathode | d. | neither |
|
|
|
37.
|
At which electrode (anode or cathode) does oxidation occur in an electrolytic
cell?
a. | anode | c. | both | b. | cathode | d. | neither |
|
|
|
38.
|
Which of the following is true about an electrolytic cell?
a. | It changes electrical energy into chemical energy. | b. | It is the type of
cell used in electroplating. | c. | It uses an electric current to make a
nonspontaneous reaction go. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
39.
|
What is produced in the electrolysis of brine?
a. | chlorine gas, sodium hydroxide, and hydrogen gas | b. | chlorine gas and
hydrogen gas only | c. | chlorine gas and oxygen gas
only | d. | chlorine gas and sodium only |
|
|
|
40.
|
Identify the products formed in the net reaction of the electrolysis of
water.
a. | liquid hydrogen and oxygen gas | b. | liquid oxygen and hydrogen
gas | c. | hydrogen gas and oxygen gas | d. | aqueous hydrogen ion and hydroxyl
ion |
|
|
|
41.
|
What occurs in electroplating?
a. | deposition of a salt layer on a metal | b. | deposition of a metal layer on a
material | c. | decomposition of a metal layer | d. | decomposition of a salt
layer |
|
|
|
42.
|
In electroplating, the object to be electroplated is placed ____.
a. | at the anode | b. | at the cathode | c. | at either the anode
or cathode | d. | in between the anode and the cathode |
|