Matching (Value 4)
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | coordinate covalent bond | d. | single covalent
bond | b. | double covalent bond | e. | polar bond | c. | structural formula | f. | hydrogen bond |
|
|
|
1.
|
a depiction of the arrangement of atoms in molecules and polyatomic
ions
|
|
|
2.
|
a covalent bond in which only one pair of electrons is shared
|
|
|
3.
|
a covalent bond in which the shared electron pair comes from only one of the
atoms
|
|
|
4.
|
a type of bond that is very important in determining the properties of water
and of important biological molecules such as proteins and DNA
|
Multiple Choice (Value 10) + one bonus
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers
the question.
|
|
|
5.
|
Which is a typical characteristic of an ionic compound?
a. | Electron pairs are shared among atoms. | b. | The ionic compound has a low solubility in
water. | c. | The ionic compound is described as a molecule. | d. | The ionic compound
has a high melting point. |
|
|
|
6.
|
What is shown by the structural formula of a molecule or polyatomic ion?
a. | the arrangement of bonded atoms | c. | the number of metallic
bonds | b. | the number of ionic bonds | d. | the shapes of molecular orbitals |
|
|
|
7.
|
Which of these elements does not exist as a diatomic molecule?
|
|
|
8.
|
How do atoms achieve noble-gas electron configurations in single covalent
bonds?
a. | One atom completely loses two electrons to the other atom in the
bond. | b. | Two atoms share two pairs of electrons. | c. | Two atoms share two
electrons. | d. | Two atoms share one electron. |
|
|
|
9.
|
Why do atoms share electrons in covalent bonds?
a. | to become ions and attract each other | b. | to attain a noble-gas electron
configuration | c. | to become more polar | d. | to increase their atomic
numbers |
|
|
|
10.
|
Which of the following is the name given to the pairs of valence electrons that
do not participate in bonding in diatomic oxygen molecules?
a. | unvalenced pair | c. | inner pair | b. | outer pair | d. | unshared pair |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which of the following electron configurations gives the correct arrangement of
the four valence electrons of the carbon atom in the molecule methane (CH 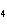 )?
|
|
|
12.
|
Which of the following diatomic molecules is joined by a double covalent
bond?
|
|
|
13.
|
When H 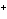 forms a bond with H 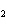 O to form the hydronium
ion H 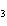 O 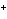 , this bond is called a coordinate covalent bond because
____. a. | both bonding electrons come from the oxygen atom | b. | it forms an
especially strong bond | c. | the electrons are equally
shared | d. | the oxygen no longer has eight valence electrons |
|
|
|
14.
|
How many valid electron dot formulas—having the same number of electron
pairs for a molecule or ion—can be written when a resonance structure occurs?
a. | 0 | c. | 2 only | b. | 1 only | d. | 2 or more |
|
|
|
15.
|
In which of the following compounds is the octet expanded to include 12
electrons?
|
Numeric Response (Value 4)
|
|
|
16.
|
How many valence electrons does an iodine atom have?
|
|
|
17.
|
What is the total number of covalent bonds normally associated with a single
carbon atom in a compound?
|
|
|
18.
|
How many electrons are shared in a single covalent bond?
|
|
|
19.
|
How many electrons are shared in a double covalent bond?
|