Matching (Value 19)
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | atomic orbital | d. | ground state | b. | aufbau principle | e. | Pauli exclusion principle | c. | electron
configuration | f. | Heisenberg
uncertainty principle |
|
|
|
1.
|
arrangement of electrons around atomic nucleus
|
|
|
2.
|
states the impossibility of knowing both velocity and position of a moving
particle at the same time
|
|
|
3.
|
each orbital has at most two electrons
|
|
|
4.
|
region of high probability of finding an electron
|
|
|
5.
|
lowest energy level
|
|
|
6.
|
tendency of electrons to enter orbitals of lowest energy first
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | network solid | e. | tetrahedral angle | b. | bonding orbital | f. | VSEPR theory | c. | dipole
interaction | g. | sigma
bond | d. | bond dissociation energy |
|
|
|
7.
|
molecular orbital that can be occupied by two electrons of a covalent
bond
|
|
|
8.
|
attraction between polar molecules
|
|
|
9.
|
crystal in which all the atoms are covalently bonded to each other
|
|
|
10.
|
energy needed to break a single bond between two covalently bonded
atoms
|
|
|
11.
|
symmetrical bond along the axis between the two nuclei
|
|
|
12.
|
shapes adjust so valence-electron pairs are as far apart as possible
|
|
|
13.
|
109.5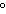
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | atomic emission spectrum | d. | photon | b. | frequency | e. | quantum | c. | wavelength | f. | spectrum |
|
|
|
14.
|
energy needed to move an electron from one energy level to another
|
|
|
15.
|
distance between wave crests
|
|
|
16.
|
separation of light into different wavelengths
|
|
|
17.
|
discrete bundle of electromagnetic energy
|
|
|
18.
|
number of wave cycles passing a point per unit of time
|
|
|
19.
|
frequencies of light emitted by an element
|
Multiple Choice (Value 19 bonus questions)
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers
the question.
|
|
|
20.
|
Which of the following gases is the best choice for inflating a balloon that
must remain inflated for a long period of time?
a. | neon | c. | oxygen | b. | hydrogen | d. | argon |
|
|
|
21.
|
How does atomic radius change from left to right across a period in the periodic
table?
a. | It first decreases, then increases. | c. | It first increases, then
decreases. | b. | It tends to increase. | d. | It tends to decrease. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Why is the second ionization energy greater than the first ionization
energy?
a. | It is more difficult to remove a second electron from an atom. | b. | The nuclear
attraction from protons in the nucleus decreases. | c. | The size of atoms increases down a
group. | d. | The size of anions decreases across a period. |
|
|
|
23.
|
What is the shape of a molecule with a triple bond?
a. | bent | c. | linear | b. | tetrahedral | d. | pyramidal |
|
|
|
24.
|
Which of the following bond types is normally the weakest?
a. | sigma bond formed by the overlap of one s and one p
orbital | b. | sigma bond formed by the overlap of two s orbitals | c. | pi bond formed by
the overlap of two p orbitals | d. | sigma bond formed by the overlap of two p
orbitals |
|
|
|
25.
|
The quantum mechanical model of the atom ____.
a. | involves the probability of finding an electron in a certain
position | b. | has many analogies in the visible world | c. | was proposed by
Niels Bohr | d. | defines the exact path of an electron around the
nucleus |
|
|
|
26.
|
Which of the following factors contributes to the increase in ionization energy
from left to right across a period?
a. | an increase in the number of protons | b. | an increase in the size of the
nucleus | c. | an increase in the shielding effect | d. | fewer electrons in the highest occupied energy
level |
|
|
|
27.
|
What type of hybrid orbital exists in the methane molecule?
|
|
|
28.
|
What is the element with the highest electronegativity value?
a. | helium | c. | fluorine | b. | cesium | d. | calcium |
|
|
|
29.
|
Who predicted that all matter can behave as waves as well as particles?
a. | Albert Einstein | c. | Max Planck | b. | Louis de Broglie | d. | Erwin
Schrodinger |
|
|
|
30.
|
Which of the following quantum leaps would be associated with the greatest
energy of emitted light?
a. | n = 5 to n = 4 | c. | n = 4 to n = 5 | b. | n = 2 to n = 5 | d. | n = 5 to n = 1 |
|
|
|
31.
|
Which of the following electromagnetic waves have the highest frequencies (short
wavelength)?
a. | ultraviolet light waves | c. | gamma rays | b. | microwaves | d. | X-rays |
|
|
|
32.
|
Which of the following elements has the smallest atomic radius?
a. | bromine | c. | selenium | b. | chlorine | d. | sulfur |
|
|
|
33.
|
What is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in the gaseous
state called?
a. | electronegative energy | c. | nuclear energy | b. | ionization energy | d. | shielding
energy |
|
|
|
34.
|
Which of the following elements has the lowest electronegativity?
a. | fluorine | c. | carbon | b. | lithium | d. | bromine |
|
|
|
35.
|
How are the frequency and wavelength of light related?
a. | They are inversely proportional to each other. | b. | Frequency equals
wavelength divided by the speed of light. | c. | They are directly proportional to each
other. | d. | Wavelength is determined by dividing frequency by the speed of
light. |
|
|
|
36.
|
Which of the following gases will effuse the most rapidly?
a. | bromine | c. | ammonia | b. | hydrogen | d. | chlorine |
|
|
|
37.
|
If oxygen is removed from a sample of air as iron rusts, what happens to the
partial pressure of oxygen in the air?
a. | It decreases. | c. | The change cannot be determined. | b. | It
increases. | d. | It stays the
same. |
|
|
|
38.
|
Which elements can form diatomic molecules joined by a single covalent
bond?
a. | hydrogen only | b. | halogens only | c. | halogens and members
of the oxygen group only | d. | hydrogen and the halogens
only |
|
Short Answer: Show all work including formulas and units (Value 3)
|
|
|
39.
|
What is the frequency of ultraviolet light with wavelength 2.94 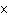
10 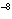 m? ( c = 3.00 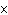 10 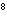 m/s)
|
Essay: Complete one of the following. (Value 3)
|
|
|
40.
|
Describe the trends in electronegativity within groups and across periods in the
periodic table. Provide examples.
|
|
|
41.
|
Indicate how bonding is explained in terms of molecular orbitals.
|
|
|
42.
|
What is the quantum mechanical model?
|
|
|
43.
|
Can some atoms exceed the limits of the octet rule in bonding? If so, give an
example.
|