Matching
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | atomic orbital | d. | ground state | b. | aufbau principle | e. | Pauli exclusion principle | c. | electron
configuration | f. | Heisenberg
uncertainty principle |
|
|
|
1.
|
region of high probability of finding an electron
|
|
|
2.
|
states the impossibility of knowing both velocity and position of a moving
particle at the same time
|
|
|
3.
|
lowest energy level
|
|
|
4.
|
tendency of electrons to enter orbitals of lowest energy first
|
|
|
5.
|
arrangement of electrons around atomic nucleus
|
|
|
6.
|
each orbital has at most two electrons
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | halide ion | e. | valence electron | b. | octet rule | f. | coordination number | c. | ionic
bond | g. | metallic
bond | d. | electron dot structure |
|
|
|
7.
|
an electron in the highest occupied energy level of an atom
|
|
|
8.
|
Atoms react so as to acquire the stable electron structure of a noble
gas.
|
|
|
9.
|
a depiction of valence electrons around the symbol of an element
|
|
|
10.
|
an anion of chlorine or other halogen
|
|
|
11.
|
the force of attraction binding oppositely charged ions together
|
|
|
12.
|
the attraction of valence electrons for metal ions
|
|
|
13.
|
the number of ions of opposite charge surrounding each ion in a crystal
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
14.
|
In Bohr's model of the atom, where are the electrons and protons
located?
a. | The electrons move around the protons, which are at the center of the
atom. | b. | The electrons and protons move throughout the atom. | c. | The electrons occupy
fixed positions around the protons, which are at the center of the atom. | d. | The electrons and
protons are located throughout the atom, but they are not free to
move. |
|
|
|
15.
|
How does the energy of an electron change when the electron moves closer to the
nucleus?
a. | It decreases. | c. | It stays the same. | b. | It increases. | d. | It doubles. |
|
|
|
16.
|
What is the maximum number of f orbitals in any single energy level in an
atom?
|
|
|
17.
|
If three electrons are available to fill three empty 2p atomic orbitals,
how will the electrons be distributed in the three orbitals?
a. | one electron in each orbital | b. | two electrons in one orbital, one in another,
none in the third | c. | three in one orbital, none in the other
two | d. | Three electrons cannot fill three empty 2p atomic
orbitals. |
|
|
|
18.
|
What is the basis for exceptions to the aufbau diagram?
a. | Filled and half-filled energy sublevels are more stable than partially-filled energy
sublevels. | b. | Electron configurations are only probable. | c. | Electron spins are
more important than energy levels in determining electron configuration. | d. | Some elements have
unusual atomic orbitals. |
|
|
|
19.
|
Of the elements Pt, V, Li, and Kr, which is a nonmetal?
|
|
|
20.
|
The atomic number of an element is the total number of which particles in the
nucleus?
a. | neutrons | c. | electrons | b. | protons | d. | protons and
electrons |
|
|
|
21.
|
What element has the electron configuration 1 s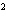 2 s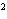 2 p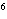 3 s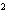 3 p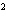 ? a. | nitrogen | c. | silicon | b. | selenium | d. | silver |
|
|
|
22.
|
Which of the following elements is a transition metal?
a. | cesium | c. | tellurium | b. | copper | d. | tin |
|
|
|
23.
|
Which of the following groupings contains only representative elements?
a. | Cu, Co, Cd | c. | Al, Mg, Li | b. | Ni, Fe, Zn | d. | Hg, Cr, Ag |
|
|
|
24.
|
Which of the following is true about the electron configurations of the
representative elements?
a. | The highest occupied s and p sublevels are completely
filled. | b. | The highest occupied s and p sublevels are partially
filled. | c. | The electrons with the highest energy are in a d sublevel. | d. | The electrons with
the highest energy are in an f sublevel. |
|
|
|
25.
|
How does atomic radius change from top to bottom in a group in the periodic
table?
a. | It tends to decrease. | c. | It first increases, then decreases. | b. | It tends to
increase. | d. | It first
decreases, then increases. |
|
|
|
26.
|
What causes the shielding effect to remain constant across a period?
a. | Electrons are added to the same principal energy level. | b. | Electrons are added
to different principal energy levels. | c. | The charge on the nucleus is constant.
| d. | The atomic radius increases. |
|
|
|
27.
|
Which of the following elements has the smallest atomic radius?
a. | sulfur | c. | selenium | b. | chlorine | d. | bromine |
|
|
|
28.
|
What is the element with the lowest electronegativity value?
a. | cesium | c. | calcium | b. | helium | d. | fluorine |
|
|
|
29.
|
As you move from left to right across the second period of the periodic table
____.
a. | ionization energy increases | c. | electronegativity
decreases | b. | atomic radii increase | d. | atomic mass decreases |
|
|
|
30.
|
Of the following elements, which one has the smallest first ionization
energy?
a. | boron | c. | aluminum | b. | carbon | d. | silicon |
|
|
|
31.
|
How many valence electrons are in an atom of phosphorus?
|
|
|
32.
|
What is the charge on the strontium ion?
a. | 2– | c. | 1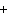 | b. | 1– | d. | 2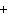 |
|
|
|
33.
|
What is the formula of the ion formed when phosphorus achieves a noble-gas
electron configuration?
|
|
|
34.
|
What is the electron configuration of the iodide ion?
|
|
|
35.
|
What is the net charge of the ionic compound calcium fluoride?
a. | 2– | c. | 0 | b. | 1– | d. | 1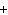 |
|
|
|
36.
|
Which of the following is true about an ionic compound?
a. | It is a salt. | c. | It is composed of anions and cations. | b. | It is held together
by ionic bonds. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
37.
|
How many valence electrons are transferred from the calcium atom to iodine in
the formation of the compound calcium iodide?
|
|
|
38.
|
Which of the following compounds has the formula KNO 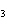 ? a. | potassium nitrate | c. | potassium nitrite | b. | potassium nitride | d. | potassium nitrogen
oxide |
|
|
|
39.
|
Which of the following pairs of elements is most likely to form an ionic
compound?
a. | magnesium and fluorine | c. | oxygen and chlorine | b. | nitrogen and sulfur | d. | sodium and
aluminum |
|
|
|
40.
|
What characteristic of metals makes them good electrical conductors?
a. | They have mobile valence electrons. | b. | They have mobile protons. | c. | They have mobile
cations. | d. | Their crystal structures can be rearranged easily. |
|
|
|
41.
|
Which metallic crystal structure has a coordination number of 8?
a. | body-centered cubic | c. | hexagonal close-packing | b. | face-centered
cubic | d. | tetragonal |
|
|
|
42.
|
Which of the following diatomic molecules is joined by a double covalent
bond?
|
|
|
43.
|
In which of the following compounds is the octet expanded to include 12
electrons?
|