Matching
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | network solid | e. | tetrahedral angle | b. | bonding orbital | f. | VSEPR theory | c. | dipole
interaction | g. | sigma
bond | d. | bond dissociation energy |
|
|
|
1.
|
energy needed to break a single bond between two covalently bonded
atoms
|
|
|
2.
|
symmetrical bond along the axis between the two nuclei
|
|
|
3.
|
molecular orbital that can be occupied by two electrons of a covalent
bond
|
|
|
4.
|
109.5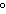
|
|
|
5.
|
shapes adjust so valence-electron pairs are as far apart as possible
|
|
|
6.
|
attraction between polar molecules
|
|
|
7.
|
crystal in which all the atoms are covalently bonded to each other
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | solvation | e. | electrolyte | b. | weak electrolyte | f. | colloid | c. | aqueous
solution | g. | surfactant | d. | solvent |
|
|
|
8.
|
interferes with hydrogen bonding between water molecules
|
|
|
9.
|
dissolving medium
|
|
|
10.
|
homogeneous mixture of water and dissolved substances
|
|
|
11.
|
Solute ions or molecules are surrounded by solvent molecules.
|
|
|
12.
|
compound that will conduct current in the liquid state or in aqueous
solution
|
|
|
13.
|
compound that ionizes incompletely in aqueous solution
|
|
|
14.
|
mixture in which particle size averages between 1 nm and 1000 nm
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | dispersed phase | e. | Tyndall effect | b. | surface tension | f. | suspension | c. | Brownian
motion | g. | solute | d. | dispersion medium | h. | emulsion |
|
|
|
15.
|
dissolved particle
|
|
|
16.
|
mixture in which particle size averages greater that 1000 nm in
diameter
|
|
|
17.
|
Colloidal particles spread throughout a suspension.
|
|
|
18.
|
phenomenon observed when beam of light passes through a colloid
|
|
|
19.
|
chaotic movement of colloidal particles
|
|
|
20.
|
colloid of a liquid in a liquid
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
21.
|
Which of the following statements is false?
a. | Knowledge of chemistry allows the public to make informed
decisions. | b. | Studying chemistry ensures that officials make correct choices in funding
technology. | c. | Knowledge of chemistry helps prepare people for careers in soil
science. | d. | Chemistry explains many aspects of nature. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Which of the following was a major contribution to chemistry by Antoine
Lavoisier?
a. | He showed that oxygen is required for material to burn. | b. | He demonstrated the
presence of phlogiston in air. | c. | He encouraged scientists to form explanations
based on philosophical arguments. | d. | He developed the science of
alchemy. |
|
|
|
23.
|
One characteristic of a scientific theory is that ____.
a. | it can never be proved | c. | it cannot be modified | b. | it can be
proved | d. | it summarizes a set
of observations |
|
|
|
24.
|
How do conceptual problems differ from numeric problems?
a. | Solutions to conceptual problems involve analysis, while numeric solutions do
not. | b. | Logic is not usually involved in solving numeric problems. | c. | A plan is necessary
to solve numeric problems, but is not necessary for conceptual problems. | d. | Solutions to
conceptual problems normally do not involve calculations. |
|
|
|
25.
|
Which of the following is a heterogeneous mixture?
a. | air | c. | steel | b. | salt water | d. | soil |
|
|
|
26.
|
Which of the following items is NOT a compound?
a. | baking soda | c. | sucrose | b. | salad dressing | d. | table salt |
|
|
|
27.
|
All of the following changes to a metal are physical changes EXCEPT ____.
a. | bending | c. | rusting | b. | melting | d. | polishing |
|
|
|
28.
|
A chemical change occurs when a piece of wood ____.
a. | is split | c. | decays | b. | is painted | d. | is cut |
|
|
|
29.
|
Which action changes the identity of the substance referenced?
a. | melting gold | b. | running an electric current through
copper | c. | corroding iron | d. | breaking an ice
cube |
|
|
|
30.
|
What happens to matter during a chemical reaction?
a. | Matter is neither destroyed or created. | b. | Some matter is
destroyed. | c. | Some matter is created. | d. | Some matter is destroyed and some is
created. |
|
|
|
31.
|
Which of the following was NOT among Democritus’s ideas?
a. | Matter consists of tiny particles called atoms. | b. | Atoms are
indivisible. | c. | Atoms retain their identity in a chemical reaction. | d. | Atoms are
indestructible. |
|
|
|
32.
|
The particles that are found in the nucleus of an atom are ____.
a. | neutrons and electrons | c. | protons and neutrons | b. | electrons only | d. | protons and
electrons |
|
|
|
33.
|
The nucleus of an atom is ____.
a. | the central core and is composed of protons and neutrons | b. | positively charged
and has more protons than neutrons | c. | negatively charged and has a high
density | d. | negatively charged and has a low density |
|
|
|
34.
|
Which of the following sets of symbols represents isotopes of the same
element?
|
|
|
35.
|
How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated?
a. | Add the number of electrons and protons together. | b. | Subtract the number
of electrons from the number of protons. | c. | Subtract the number of protons from the mass
number. | d. | Add the mass number to the number of electrons. |
|
|
|
36.
|
Which of the following equals one atomic mass unit?
a. | the mass of one electron | b. | the mass of one helium-4
atom | c. | the mass of one carbon-12 atom | d. | one-twelfth the mass of one carbon-12
atom |
|
|
|
37.
|
Which of the following statements is NOT true?
a. | Protons have a positive charge. | b. | Electrons are negatively charged and have a
mass of 1 amu. | c. | The nucleus of an atom is positively charged. | d. | Neutrons are located
in the nucleus of an atom. |
|
|
|
38.
|
Which of the following is necessary to calculate the atomic mass of an
element?
a. | the atomic mass of carbon-12 | b. | the atomic number of the
element | c. | the relative masses of the element’s protons and neutrons | d. | the masses of each
isotope of the element |
|
|
|
39.
|
How many energy sublevels are in the second principal energy level?
|
|
|
40.
|
What is the maximum number of d orbitals in a principal energy
level?
|
|
|
41.
|
According to the aufbau principle, ____.
a. | an orbital may be occupied by only two electrons | b. | electrons in the
same orbital must have opposite spins | c. | electrons enter orbitals of highest energy
first | d. | electrons enter orbitals of lowest energy first |
|
|
|
42.
|
Which of the following electromagnetic waves have the highest
frequencies?
a. | ultraviolet light waves | c. | microwaves | b. | X-rays | d. | gamma rays |
|
|
|
43.
|
The light given off by an electric discharge through sodium vapor is
____.
a. | a continuous spectrum | c. | of a single wavelength | b. | an emission
spectrum | d. | white
light |
|
|
|
44.
|
As changes in energy levels of electrons increase, the frequencies of atomic
line spectra they emit ____.
a. | increase | c. | remain the same | b. | decrease | d. | cannot be
determined |
|
|
|
45.
|
The atomic emission spectra of a sodium atom on Earth and of a sodium atom in
the sun would be ____.
a. | the same | b. | different from each other | c. | the same as those of
several other elements | d. | the same as each other only in the ultraviolet
range |
|
|
|
46.
|
How do the energy differences between the higher energy levels of an atom
compare with the energy differences between the lower energy levels of the atom?
a. | They are greater in magnitude than those between lower energy
levels. | b. | They are smaller in magnitude than those between lower energy
levels. | c. | There is no significant difference in the magnitudes of these
differences. | d. | No answer can be determined from the information
given. |
|
|
|
47.
|
Who predicted that all matter can behave as waves as well as particles?
a. | Albert Einstein | c. | Max Planck | b. | Erwin Schrodinger | d. | Louis de
Broglie |
|
|
|
48.
|
The wavelike properties of electrons are useful in ____.
a. | defining photons | b. | writing electron
configurations | c. | magnifying objects | d. | determining the velocity and position of a
particle |
|
|
|
49.
|
In an s orbital, the probability of finding an electron a particular
distance from the nucleus does NOT depend on ____.
a. | a quantum mechanical model | c. | the Schrodinger
equation | b. | direction with respect to the nucleus | d. | the electron energy
sublevel |
|
|
|
50.
|
Each period in the periodic table corresponds to ____.
a. | a principal energy level | c. | an orbital | b. | an energy
sublevel | d. | a
suborbital |
|
|
|
51.
|
The modern periodic table is arranged in order of increasing atomic ____.
a. | mass | c. | number | b. | charge | d. | radius |
|
|
|
52.
|
Which of the following categories includes the majority of the elements?
a. | metalloids | c. | metals | b. | liquids | d. | nonmetals |
|
|
|
53.
|
Of the elements Pt, V, Li, and Kr, which is a nonmetal?
|
|
|
54.
|
Elements that are characterized by the filling of p orbitals are
classified as ____.
a. | groups 3A through 8A | c. | inner transition metals | b. | transition
metals | d. | groups 1A and
2A |
|
|
|
55.
|
Which of the following groupings contains only representative elements?
a. | Cu, Co, Cd | c. | Al, Mg, Li | b. | Ni, Fe, Zn | d. | Hg, Cr, Ag |
|
|
|
56.
|
In which of the following groups of ions are the charges all shown
correctly?
|
|
|
57.
|
What is the element with the highest electronegativity value?
a. | cesium | c. | calcium | b. | helium | d. | fluorine |
|
|
|
58.
|
Which statement is true about electronegativity?
a. | Electronegativity is the ability of an anion to attract another
anion. | b. | Electronegativity generally increases as you move from top to bottom within a
group. | c. | Electronegativity generally is higher for metals than for
nonmetals. | d. | Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a
period. |
|
|
|
59.
|
Which of the following factors contributes to the increase in ionization energy
from left to right across a period?
a. | an increase in the shielding effect | b. | an increase in the size of the
nucleus | c. | an increase in the number of protons | d. | fewer electrons in the highest occupied energy
level |
|
|
|
60.
|
As you move from left to right across the second period of the periodic table
____.
a. | ionization energy increases | c. | electronegativity
decreases | b. | atomic radii increase | d. | atomic mass decreases |
|
|
|
61.
|
Of the following elements, which one has the smallest first ionization
energy?
a. | boron | c. | aluminum | b. | carbon | d. | silicon |
|
|
|
62.
|
What is the charge on the strontium ion?
a. | 2– | c. | 1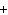 | b. | 1– | d. | 2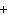 |
|
|
|
63.
|
What is the formula of the ion formed when potassium achieves noble-gas electron
configuration?
|
|
|
64.
|
What is the electron configuration of the iodide ion?
|
|
|
65.
|
Ionic compounds are normally in which physical state at room temperature?
a. | solid | c. | gas | b. | liquid | d. | plasma |
|
|
|
66.
|
Under what conditions can potassium bromide conduct electricity?
a. | only when melted | b. | only when dissolved | c. | only when it is in
crystal form | d. | only when melted or dissolved in water |
|
|
|
67.
|
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of most ionic compounds?
a. | They are solids. | b. | They have low melting
points. | c. | When melted, they conduct an electric current. | d. | They are composed of
metallic and nonmetallic elements. |
|
|
|
68.
|
When one atom contributes both bonding electrons in a single covalent bond, the
bond is called a(n) ____.
a. | one-sided covalent bond | c. | coordinate covalent
bond | b. | unequal covalent bond | d. | ionic covalent bond |
|
|
|
69.
|
Molecular orbital theory is based upon which of the following models of the
atom?
a. | classical mechanical model | c. | quantum mechanical
model | b. | Bohr model | d. | Democritus’s model |
|
|
|
70.
|
The side-by-side overlap of p orbitals produces what kind of bond?
a. | alpha bond | c. | pi bond | b. | beta bond | d. | sigma bond |
|
|
|
71.
|
Sigma bonds are formed as a result of the overlapping of which type(s) of atomic
orbital(s)?
a. | s only | c. | d only | b. | p only | d. | s and
p |
|
|
|
72.
|
Which of the following theories provides information concerning both molecular
shape and molecular bonding?
a. | molecular orbital theory | c. | orbital hybridization
theory | b. | VSEPR theory | d. | Bohr atomic theory |
|
|
|
73.
|
What type of hybridization occurs in the orbitals of a carbon atom participating
in a triple bond with another carbon atom?
|
|
|
74.
|
As the temperature of the gas in a balloon decreases, which of the following
occurs?
a. | The volume of the balloon increases. | b. | The average kinetic energy of the gas
decreases. | c. | The gas pressure inside the balloon increases. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
75.
|
Charles's law states that ____.
a. | the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its temperature in
kelvins | b. | the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature in
kelvins | c. | the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature in
kelvins | d. | the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its temperature in
kelvins |
|
|
|
76.
|
When the pressure and number of particles of a gas are constant, which of the
following is also constant?
a. | the sum of the volume and temperature in kelvins | b. | the difference of
the volume and temperature in kelvins | c. | the product of the volume and temperature in
kelvins | d. | the ratio of the volume and temperature in kelvins |
|
|
|
77.
|
As the temperature of a fixed volume of a gas increases, the pressure will
____.
a. | vary inversely | c. | not change | b. | decrease | d. | increase |
|
|
|
78.
|
At a certain temperature and pressure, 0.20 mol of carbon dioxide has a volume
of 3.1 L. A 3.1-L sample of hydrogen at the same temperature and pressure ____.
a. | has the same mass | b. | contains the same number of
atoms | c. | has a higher density | d. | contains the same number of
molecules |
|
|
|
79.
|
At low temperatures and pressures, how does the volume of a real gas compare
with the volume of an ideal gas under the same conditions?
a. | It is greater. | c. | There is no difference. | b. | It is
less. | d. | It depends on the
type of gas. |
|
|
|
80.
|
Which of the following gases will effuse the most rapidly?
a. | bromine | c. | ammonia | b. | chlorine | d. | hydrogen |
|
|
|
81.
|
The bonds between the hydrogen and oxygen atoms in a water molecule are
____.
a. | hydrogen bonds | c. | nonpolar covalent bonds | b. | ionic
bonds | d. | polar covalent
bonds |
|
|
|
82.
|
Which of the following is NOT a common hydrate?
a. | Epsom salt | c. | sugar | b. | borax | d. | alum |
|
|
|
83.
|
Which compound changes color when it becomes a hydrate?
a. | silicon dioxide | c. | copper(II) sulfate | b. | sodium chloride | d. | potassium
chloride |
|
|
|
84.
|
Which of the following mixtures is NOT a colloid?
a. | fog | c. | paint | b. | milk | d. | sugar water |
|
|
|
85.
|
Which of the following types of mixtures exhibit the Tyndall effect?
a. | suspensions and colloids | c. | colloids and
solutions | b. | suspensions and solutions | d. | colloids only |
|
|
|
86.
|
Which of these statements is correct?
a. | Particles can be filtered from a suspension. | b. | A solution is
heterogeneous. | c. | A colloidal system does not exhibit the Tyndall effect. | d. | The particles in a
colloidal system are affected by gravity. |
|
|
|
87.
|
Which of the following pairs of factors affects the solubility of a particular
substance?
a. | temperature and the nature of solute and solvent | b. | temperature and
degree of mixing | c. | particle size and degree of mixing | d. | particle size and
temperature |
|
|
|
88.
|
In which of the following is the solution concentration expressed in terms of
molarity?
|
|
|
89.
|
The volume of 6.00M HCl needed to make 319 mL of 6.80M HCl is
____.
a. | 0.128 mL | c. | 281 mL | b. | 7.8 mL | d. | 362 mL |
|
|
|
90.
|
What is the approximate molar mass of a molecular solute if 300 g of the solute
in 1000 g of water causes the solution to have a boiling point of 101 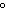 C?
( K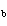 = 0.512 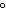 C/m;
K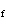 = 1.86 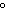 C/ m; molar
mass of water = 18 g) a. | 15 amu | c. | 150 amu | b. | 30 amu | d. | 300 amu |
|
Short Answer
|
|
|
91.
|
In which group in the periodic table do the elements have the highest
electronegativity values?
|
|
|
92.
|
Give the electron configuration for the lithium ion.
|
|
|
93.
|
A balloon filled with helium has a volume of 30.0 L at a pressure of 100 kPa and
a temperature of 15.0 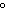 C. What will the volume of the balloon be if the
temperature is increased to 80.0 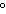 C and the pressure remains constant?
|
|
|
94.
|
What is the percentage of water in the hydrate CoCl 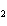  6 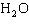 ?
|
|
|
95.
|
Calculate the molality of a solution prepared by dissolving 175 g of
KNO  in 750 g of water.
|
Numeric Response
|
|
|
96.
|
How many traditional areas of study can chemistry be divided into?
|
|
|
97.
|
How many steps are involved in solving numeric problems?
|
|
|
98.
|
About how many more times massive is a proton than an electron?
|
|
|
99.
|
What is the total number of subatomic particles in the nucleus of an atom of
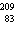 Bi?
|
|
|
100.
|
Determine the number of electrons in an atom of iridium.
|
|
|
101.
|
What is the atomic number for an element with 41 neutrons and a mass number of
80?
|
|
|
102.
|
How many electrons does the ion Ca 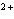 contain?
|
|
|
103.
|
How many valence electrons does an iodine atom have?
|
|
|
104.
|
How many electrons does a nitrogen atom need to gain in order to attain a
noble-gas electron configuration?
|
|
|
105.
|
How many nonbonding pairs of electrons are in a water molecule?
|