Matching (Value 13)
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | network solid | e. | tetrahedral angle | b. | bonding orbital | f. | VSEPR theory | c. | dipole
interaction | g. | sigma
bond | d. | bond dissociation energy |
|
|
|
1.
|
energy needed to break a single bond between two covalently bonded
atoms
|
|
|
2.
|
molecular orbital that can be occupied by two electrons of a covalent
bond
|
|
|
3.
|
crystal in which all the atoms are covalently bonded to each other
|
|
|
4.
|
attraction between polar molecules
|
|
|
5.
|
109.5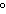
|
|
|
6.
|
shapes adjust so valence-electron pairs are as far apart as possible
|
|
|
7.
|
symmetrical bond along the axis between the two nuclei
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | coordinate covalent bond | d. | single covalent
bond | b. | double covalent bond | e. | polar bond | c. | structural formula | f. | hydrogen bond |
|
|
|
8.
|
a covalent bond in which two pairs of electrons are shared
|
|
|
9.
|
a covalent bond in which only one pair of electrons is shared
|
|
|
10.
|
a depiction of the arrangement of atoms in molecules and polyatomic
ions
|
|
|
11.
|
a type of bond that is very important in determining the properties of water
and of important biological molecules such as proteins and DNA
|
|
|
12.
|
a covalent bond between two atoms of significantly different
electronegativities
|
|
|
13.
|
a covalent bond in which the shared electron pair comes from only one of the
atoms
|
Multiple Choice (Value 9)
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers
the question.
|
|
|
14.
|
Molecular orbital theory is based upon which of the following models of the
atom?
a. | classical mechanical model | c. | quantum mechanical
model | b. | Democritus’s model | d. | Bohr model |
|
|
|
15.
|
Which of the following theories provides information concerning both molecular
shape and molecular bonding?
a. | Bohr atomic theory | c. | molecular orbital theory | b. | orbital
hybridization theory | d. | VSEPR
theory |
|
|
|
16.
|
What causes hydrogen bonding?
a. | sharing of electron pairs | b. | bonding of a covalently bonded hydrogen atom
with an unshared electron pair | c. | motion of electrons | d. | attraction between
ions |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following bond types is normally the weakest?
a. | sigma bond formed by the overlap of two p orbitals | b. | sigma bond formed by
the overlap of one s and one p orbital | c. | pi bond formed by the overlap of two p
orbitals | d. | sigma bond formed by the overlap of two s
orbitals |
|
|
|
18.
|
What is thought to cause the dispersion forces?
a. | attraction between ions | c. | differences in
electronegativity | b. | sharing of electron pairs | d. | motion of
electrons |
|
|
|
19.
|
How is a pair of molecular orbitals formed?
a. | by the reproduction of a single atomic orbital | b. | by the splitting of
a single atomic orbital | c. | by the overlap of two atomic orbitals from the
same atom | d. | by the overlap of two atomic orbitals from different
atoms |
|
|
|
20.
|
How many pi bonds are formed when sp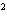 hybridization
occurs in ethene, C 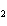 H 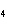 ?
|
|
|
21.
|
Which of the following covalent bonds is the most polar? Electronegative values:
(H=2.1), (F=4.0), (C=2.5) and (N=3.0)
|
|
|
22.
|
The side-by-side overlap of p orbitals produces what kind of bond?
a. | beta bond | c. | pi bond | b. | alpha bond | d. | sigma bond |
|
Numeric Response (Value 2)
|
|
|
23.
|
What is the bond angle and shape in a water molecule?
|
Problem (Bonus 1)
|
|
|
24.
|
What does VSERP stand for?
|